By: Claudia Castanheira – Communications Manager at Fashion Revolution Brasil

After two weeks of complex negotiations and over a day of delays, COP29 concluded with the resignation of the poorest and most vulnerable countries, forced to accept a climate finance deal far below the $1 trillion annually demanded by 2035. The final agreement settled on $300 billion per year for climate financing until 2035, the result of over 30 hours of tense talks and setbacks.
Countries in the Global North, including the European Union delegation, the United States, and Canada, who advocated for less ambitious targets, were widely criticized by international observers and NGOs. The European bloc was even awarded the “Fossil of the Day” on November 20, a symbolic prize given by the Climate Action Network (CAN) to those seen as blocking progress during climate talks.
It’s important to highlight that without adequate financial resources, it will be impossible for countries — particularly those in the Global South — to implement climate actions for adaptation, mitigation, and a just energy transition. This lack of funding also puts the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C at risk.
Another notable point was the lack of clear commitments to energy transition — including the phase-out of fossil fuels, a central theme of COP28 in Dubai. This objective, removed from the final document in 2023, was not explicitly reinstated in the agreement signed on Saturday, marking a victory for oil and gas-producing countries.
In a geopolitical context marked by wars and crises, achieving significant progress was expected to be a challenging task. However, the general feeling is that this COP resulted in few, if any, meaningful achievements, increasing distrust in the multilateral process to address the climate crisis.
Fashion at COP29

Fashion Revolution Brazil took part in COP29, engaging in discussions with civil society and other stakeholders to highlight the crucial role of fashion and textiles in addressing the climate crisis.
While formal negotiations left much to be desired, we came out stronger: Building new connections and forging global partnerships, which are essential for driving transformation in the industry.
As a civil movement, being part of these spaces is absolutely necessary. Even in the face of roadblocks and insufficient decisions, we reaffirmed our commitment to pursue a more transparent, fairer, and more sustainable fashion industry.
As members of the Brazilian delegation, we put forward clear demands:
For brands:
- Be transparent about how and where clothes are made, how many pieces are produced, and the social and environmental impacts of their production.
- Set ambitious targets for decarbonization and degrowth, and be clear about how these goals will be achieved.
- Publicly share updates on progress and concrete actions to meet these targets.
For policymakers:
- Develop policies to support Brazil and other garment-producing countries facing climate crises and vulnerabilities.
- Prioritize efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions in the global fashion industry.
- Ensure small suppliers and family farmers have access to financial resources to build resilience against climate change.
At the event, we presented key reports, including What Fuels Fashion, a climate-focused analysis of the Global Fashion Transparency Index, and the latest edition of the Fashion Transparency Index Brazil, which reviews six years of progress and challenges in the industry.
COP30: What is next?
 Looking ahead, our goal is to mobilize the world’s largest civil movement for fashion to come together at COP30 in Belém, Brazil. This will be a landmark event: Brazil is the world’s top exporter of cotton, yet it faces major challenges like carbon emissions from deforestation and a dependency on fossil fuels.
Looking ahead, our goal is to mobilize the world’s largest civil movement for fashion to come together at COP30 in Belém, Brazil. This will be a landmark event: Brazil is the world’s top exporter of cotton, yet it faces major challenges like carbon emissions from deforestation and a dependency on fossil fuels.
The takeaway from COP29 is clear: COP30 must tackle the issues that remain unresolved. We’ll be there in the Amazon rainforest, demanding an end to fossil-fueled fashion and advocating for the rights of those most affected by the climate crisis, often the women who make our clothes.
The fashion climate agenda is just getting started!
Standing together with #FashionforClimate
What can you (citizens) do?
HEY BIG FASHION BRANDS,
START FINANCING YOUR DECARBONISATION NOW!
COP29, the 29th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, is poised to be a pivotal event in the global fight against climate change. As usual, the conference will bring together world leaders, negotiators, and stakeholders to assess progress on climate commitments made during previous COP meetings and to discuss strategies for achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement. But we are all fatigued from discussions and commitments, the time is running out and we urgently need action.
As many stakeholders are referring to COP29 as ‘the finance COP’, with negotiations seen as critical to advance a range of financial tools and instruments to support actions to address climate change, we want to reinforce our calling on major fashion brands to invest at least 2% of their revenue in a fair transition away from fossil fuels – like coal – to renewable energy sources – like wind and solar – to power fashion’s supply chain in a clean way.
Fashion is fueling the climate crisis, and major fashion brands must urgently put their money where their emissions are.
Fashion is one of the most polluting industries on the planet, with fossil fuels burned at every stage of production. The industry alone is set to overshoot the 1.5°C limit by 50%, doubling emissions rather than halving them as the science is crying out for. Frequent climate catastrophes, like extreme heat, flooding, and droughts are devastating the livelihoods of workers across global garment supply chains, with extreme weather estimated to cost nearly one million jobs by 2030.
Fashion Revolution’s new report, What Fuels Fashion? reviewed 250 of the world’s largest fashion brands and retailers and ranked them according to their level of disclosure on climate and energy-related data in their operations and supply chains. The findings revealed that major fashion brands aren’t doing enough to cut fossil fuel use in their supply chains. 86% of major fashion brands lack a public coal phase-out target, and only 3% disclose the level of financial support provided to supply chain workers affected by the climate crisis.
By investing at least 2% of their revenue into clean, renewable energy and upskilling and supporting workers, fashion could simultaneously curb the impacts of the climate crisis and reduce poverty and inequality within their supply chains. Climate breakdown is avoidable because we have the solution – and big fashion can certainly afford it.
Our Demands for Fashion Brands:
- Tell us about your clothes: How and where they were made, how many were produced.
-
- Disclose your annual production volumes
- Disclose the fiber mix of your clothes and why are these fibers
- Disclose the prices you pay to suppliers for each item and the wages that workers receive for the production of your garments
- Tell us about your impact: Measure your environmental and social impact and disclose it.
- Disclose your supplier lists (Tier 1 and Tier 2) in an open source easy to usee for others (such as excel, csv or json)
- Disclose your fuel mix across your supply chains by country
- Publish a detailed breakdown of renewable energy procurement type in your operations and supply chain
- Tell us how you are leveraging your power to influence and advocate for a decarbonisation process and just transition in your supplying countries
- Tell us about your targets: Set targets, disclose how you established them, how you plan to meet them, and report on progress.
- Disclose your climate targets, including your supply chain, backed up by a decarbonisation strategy. Oh and don’t forget to share how were suppliers consulted in the establishment of those targets.
- Publish evidence of climate action in the supply chain and how these efforts are reducing greenhouse gas emissions while increasing renewable energy capacity.
- Share how you are supporting your suppliers for a just transition
Our Demands for Policymakers:
- Implement Binding Regulations: Require transparency and corporate accountability on environmental and human rights issues in the global fashion industry.
- Responsible Purchasing Practices: Ensure brand payments to suppliers reflect the true costs of sustainable production.
- Finance the Green Transition: Develop policies that support garment-producing countries facing debt crises and climate vulnerabilities, prioritizing actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Direct Financial Support for Suppliers: Facilitate access to financial resources for suppliers to enhance resilience to climate change, with flexible repayment terms and simplified loan processes.
- Equitable Decision-Making Models: Create decision-making frameworks informed by affected stakeholders, ensuring local contexts and regional needs are integrated into climate action planning and implementation.
What can you (citizens) do?
- You can read the What Fuels Fashion report here and share!
- Email your brands here
- Donate here to keep our revolution going
IT’S TIME FOR FASHION BRANDS TO PUT THEIR MONEY WHERE THEIR EMISSIONS ARE
Fashion Revolution, the world’s largest fashion activism movement, is at Climate Week NYC 2024 with a clear message: fashion is fueling the climate crisis, and major fashion brands must urgently put their money where their emissions are.
We’re calling on major fashion brands to invest at least 2% of their revenue in a fair transition away from fossil fuels – like coal – to renewable energy sources – like wind and solar – to power fashion’s supply chain in a clean way.
Fashion is one of the most polluting industries on the planet, with fossil fuels burned at every stage of production. The industry alone is set to overshoot the 1.5°C limit by 50%, doubling emissions rather than halving them as the science is crying out for. Frequent climate catastrophes, like extreme heat, flooding, and droughts are devastating the livelihoods of workers across global garment supply chains, with extreme weather estimated to cost nearly one million jobs by 2030.
Fashion Revolution’s new report, What Fuels Fashion? reviewed 250 of the world’s largest fashion brands and retailers and ranked them according to their level of disclosure on climate and energy-related data in their operations and supply chains. The findings revealed that major fashion brands aren’t doing enough to cut fossil fuel use in their supply chains. 86% of major fashion brands lack A PUBLIC coal phase-out target, and only 3% disclose the level of financial support provided to supply chain workers affected by the climate crisis.
By investing at least 2% of their revenue into clean, renewable energy and upskilling and supporting workers, fashion could simultaneously curb the impacts of the climate crisis and reduce poverty and inequality within their supply chains. Climate breakdown is avoidable because we have the solution – and big fashion can certainly afford it.
WE ARE CALLING ON
- Policymakers to enhance regulation
- Investors to fund and co-fund renewable energy and decarbonisation projects
- Citizens to use their voice- email major brands and retailers and call on them to invest at least 2% of their annual revenues into their decarbonisation and Just Transition efforts
- Civil society, academia, journalists to leverage data and findings to scrutinise and verify the public claims made by brands
Big fashion can no longer mask its lack of decarbonisation progress with vague, insufficient targets and pilot projects that fail to benefit most of the supply chain. The need for system change is undeniable. It’s time for brands to put their money where their emissions are.
You can read the report here. Email your brands here.Covid-19 was not going to come in the way of Fashion Open Studio 2020 and its audience. If anything, the pandemic gave this year’s designers a greater audience than ever. The studio tours, workshops and conversations were pivoted to a digital format, allowing us to #StayHome while also staying connected with the creative community making use of this time to rethink systems, supply chains and resources.
Sustainability means many things
We celebrated the work of 53 designers across 14 countries including Iran, New Zealand, Vietnam, Nigeria, Zimbabwe, Switzerland and Germany. There was so much to learn from the designers who took part, each one with solutions to the challenges most pressing to them. At Fashion Open Studio we understand that sustainability means many things (and sometimes, nothing at all). Every designer taking part in this programme is finding solutions that will help to move their own business forward without over stretching the planet’s resources and with respect for artisans and garment workers who craft and stitch their collections. The purpose of Fashion Open Studio is to share these stories and help them to reach the audiences they deserve.

From Fashion Revolution’s incredible global network there were so many eloquent voices, with as many different perspectives on how clothing should be made and valued. From Zimbabwe, Fashion Revolution’s country coordinator Rudo Nondo talked to Julian Tamuka about his brand Guyllelujah. Julian had previously not considered ideas about sustainability until he was introduced to Fashion Revolution through Fashion Open Studio and realised his use of limited resources – deadstock materials and off cuts – and his philosophy of making staple items of clothing because as he says “it’s a staple for a reason, it’s more likely to be of value and stick around longer,” is the way he works out of necessity.
I recommend everyone watches his short video, The New Philosophy of Fashion as there is so much to learn from his approach.
Likewise, from Harare, Haus of Stone presented Therapy of Fashion, which combined mediation and making one session of mindfulness and creativity. The brand’s founder, Danayi, led us through a fusion of yoga; traditional mbira music and hand sewing. Participants are invited to send the roses they make in the workshop to become part of a collective scarf called ‘Hope’.
View this post on Instagram
In Switzerland in collaboration with Mode Suisse, Rafael Kouto asked “What is Upcycling? And what is waste?” Rafael showed how to ‘pimp’ your garments with an introduction on his upcycling practice and so much information and advice on rethinking and valuing the contents of your own wardrobe. It’s a really wonderful and informative session.

From Pune in India, Karishma Shahani Khan invited small groups into a virtual studio each day to learn quilting, embroidery and hand sewing techniques in a series of sewing circles with the team from Ka Sha and the artisans they work with. They wanted to share the inherent social setting of storytelling and conversations that they witness within their everyday working environment with guests.

Also in India, in Jaipura in Rajasthan, Iro-Iro showed their practice around implementing zero-waste for their MoonWash collection, focusing on New Heroes with illustrations and readings celebrating women throughout history who have been independent thinkers and doers.
If you missed these remarkable stories, they are still available as a series of readings of letters to women from Cleopatra to the spy princess Noor Inayat Khan, and there is a collection of clothes inspired by each of them.
Vietnamese brand Tamay & Me introduced Mien artisan and co-founder Tamay from Ta Phin village in Sapa,

with a special film screening followed by a Q&A with her co-founder Hannah Cowie to explain how they work together and the heritage of the unique craftsmanship that goes into every garment.
Creativity in lockdown thrived
While the world was in lockdown, many designers still had access to their studios, either because they live in the same space, or because they were using them to continue working at a safe social distance in the essential work of making PPE and hospital scrubs as many of the Fashion Open Studio network were doing. Phoebe English talked to us from her Deptford Creek studio in south London, explaining how to quilt with waste using her paper templates.

As she spoke, the scrubs she had been making were being counted and packed up ready to be delivered to hospitals in need as part of the Emergency Designer Network with fellow FOS designer Bethany Williams. Elliss Solomon, founder of Elliss, took time out from her work for Scrub Up for the NHS to talk us through her workshop on collage – a key part of her creative development when she is designing a collection. Many others taking part in the week were playing their part in making masks, scrubs and PPE and of course, the week’s events were a great way for people to spread the word, stay connected, and share the challenges of trying to keep business going.
Collaboration makes sense
While there are designers who are still fledgling brands, this is a particularly difficult time for those newly graduated. Among the thousands of fashion graduates unable to even show their final collections as part of a degree show, we showcased the work of two emerging talents who had shown their collections as part of the Central Saint Martins MA show in March, just a week before the lockdown. The portfolio visits traditionally held for industry experts to head hunt talent, were cancelled, with future job prospects on hold for many. Matthew Needham, who temporarily joined the Fashion Revolution team for the week to help on production and Zoom management, talked us through his final collection ØYEBLIKK / 2020 ‘IN THE BLINK OF AN EYE’.
View this post on Instagram
While Needham is an advocate of waste management – a master of using trash as a precious resource in his collections – he is also becoming expert in collaboration, and is sure that this is the way forward. For his session, he brought together his co-collaborators Sneaker artist Helen Kirkum, Biotech materials researcher Alice Potts and experimental milliner Jo Miller. Together they explained some of their processes and how working collectively is a great way to consolidate sustainable thinking, encourage innovation and help lift each other’s practice and find new audiences.
Somerset House x Young Creatives
Fellow CSM MA graduate Paolo Carzana moved back to his hometown in Cardiff, Wales, the week he was supposed to be showing his final collection to the world. Paolo was chosen as the finale to the degree show, with The Boy Who Came Back to Life, a collection packed with details, extraordinary materials, botanical dyes, Pinatex textiles, and layers of story-telling, autobiographical notes, and months’ worth of research.

For his session which was part of the afternoon of events in partnership with Somerset House and its Young Creatives programme, Carzana talked from the balcony of his flat overlooking the Cardiff stadium which was at the time, being turned into a Nightingale hospital. He had made a special film, A Self Isolation Waltz for the event showing his collection against the backdrop of the building site below, and talked through his sketches, fabric swatches and references. He also talked about his plans to make a capsule collection for the planned digital London Fashion Week in June, re-using pieces from his previous work. The pandemic has forced him to rethink how he is going to work and sell – and be even more resourceful creative and sustainable as a business going forward.
Also taking part in the Somerset House programme were Bethany Williams, Katie Jones and Congregation Design. Bethany was part of a week-long series of events to celebrate the anniversary of Earth Day, planned with Somerset House long before the pandemic took hold. You can watch highlights of the day here.
There is so much to learn from the 2020 Fashion Open Studio designers. We are still absorbing and catching up with so many incredible and diverse sessions. The digital programme allowed these small, intimate studio conversations and workshops to be viewed by a global audience creating conversations that reverberated between designers and communities that hadn’t previously connected.
We are starting to plan for Fashion Open Studio 2021 and will be announcing how to apply to take part in the coming months. Until then, do spend some time watching the videos on our YouTube playlist and share the knowledge and the work of these change maker designers far and wide.
To stay up to date with Fashion Open Studio, subscribe to the Fashion Revolution youtube channel and follow Fashion Open Studio on instagram, twitter and facebook.
Can work in the garment industry lift women up? We speak to two pioneers making this happen around the globe.

First up, Colleen Clines, one half the sister duo behind Anchal Project, tells us about their journey to creating a global business that lifts women up. It all began in 2009, says Colleen, “While in India, I was introduced to the exploitive world of the commercial sex trade and the extreme lack of opportunity for women in the community. It was in this moment I was inspired to design more than beautiful landscapes, determined to create positive social and environmental change using design.”
Today, Anchal Project works across India and the USA to both train artisans and create projects that generate a meaningful and empowering income for women in both countries. Their Stitch by Stitch program in Ajmer, India operates within a hub of commerical sex work, offereing a different path for women with limited opportunities who are vulnerable to sex work and abuse.
Colleen says, “85% of Anchal artisans answered that they had joined the commercial sex trade because there was no existing alternative. If the choice to be a commercial sex worker belonged to them, it was a helpless, desperate decision amidst a financial crisis. The average artisan tried leaving the sex trade two or more times, but returned because she was unable to earn a living. Some of the artisans shared that they tried to leave upwards of five times.”
On the other side of the world, in Louisville, Kentucky, women who are recovering or vulnerable to Kentucky’s high rates of sexual violence can take part in their educational workshops, financial planning, and stress management alongside product creation and making skills.
“We felt compelled to take the project beyond the classroom with the conviction that our design training, in collaboration with local leadership, could address seemingly intractable social and environmental systems. The women we met became our sisters, sisters we had to fight for”, says Colleen.
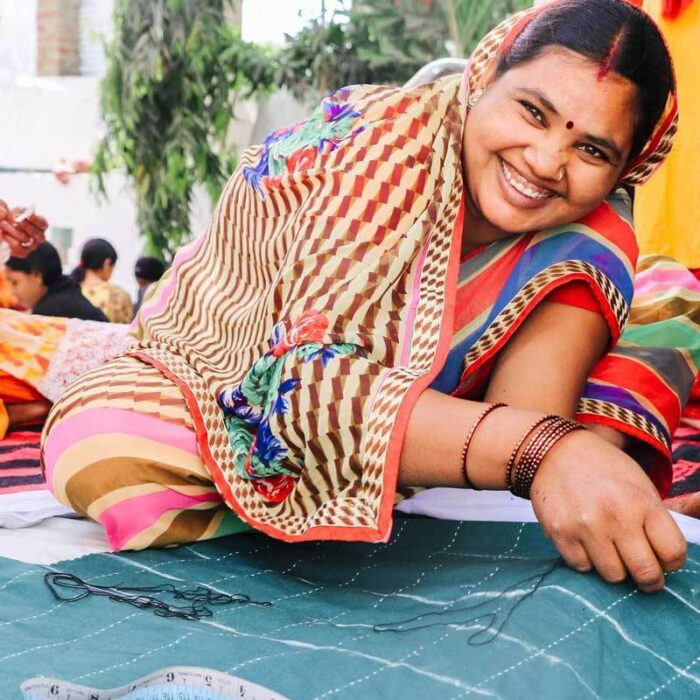

Like Anchal Project, SOKO Kenya is a fashion brand that exists with decent work as the foundation. Jo Maiden, the founder, tells us how the brand originated to solve a problem.
“I first visited Kenya with Dave, my husband, in 2007 on a trip with Ethical Fashion Forum. We both fell in love with the country and saw an opportunity to create sustainable change through fashion. We wanted to develop a creative, long-term solution to the high levels of unemployment in the local community.”
Like the wider industry, SOKO’s workforce is largely made up of women. Yet while the mainstream fashion industry often oppresses its heavily female workforce, SOKO came about to change the system.
“Our three production supervisors are women and have been with me since the beginning of SOKO Kenya in 2009”, says Jo. “We hope that having women in management positions is motivational for other women in the factory and encourages them to take the steps required to progress in their career”. She adds that “When a new employee joins SOKO Kenya, we make sure that they have set up their own bank account as a starting point. Throughout the year they are also offered various financial trainings to encourage independent saving and spending.”
If this doesn’t seem radical, it’s worth considering that around the globe, only 58% of women report having a bank account, while that number is 65% for men (World Bank, 2015).
And, like Anchal Project, the brand isn’t just about making things, but about teaching skills. “Our Stitching Academy was born out of SOKO Kenya’s need to employ more people but no one had the right skillset. We wanted to offer a comprehensive training for in the community (and now beyond) that would allow locals to be able to work as a machinist in any factory in the country, not just SOKO Kenya. This means offering training on a variety of different machines and specialities, including cutting and quality control, so that we increase their chances of being employed.”

As we consider how the fashion industry can rethink its oppressive systems, and put an end to gender equality, these considerations of education and training, decent work, living wages, and financial literacy are some of the greatest pillars to lift up women and improve lives.
A new report by Changing Markets Foundation, ‘Dirty Fashion Disrupted’, reveals that while some fashion brands and leading viscose producers are making progress to clean up dirty viscose manufacturing, the majority of brands simply continue to talk about sustainability with no evidence of action.
WHAT IS VISCOSE?
In simple terms, viscose is a cellulosic fibre which is made from wood pulp. This means that the material has a major impact on deforestation and requires a strenuous, and often heavily polluting, chemical process to turn the raw material (wood) into textiles for clothing. It’s this chemical production process that Changing Markets is trying to clean up.

Viscose is the third most commonly used fibre in the world and it has the potential to be a sustainable alternative to oil-based synthetics. Yet, previous Dirty Fashion investigations found clear evidence of viscose producers dumping untreated wastewater, contaminating waterways and ecosystems, and causing severe health impacts to local communities.
A toxic and endocrine-disrupting chemical, carbon disulphide (CS2), used in the viscose manufacturing process has been linked to serious health conditions, most notoriously as a cause of mental illness in factory workers but also a wide range of other conditions ranging from kidney disease to heart attacks and strokes.
DIRTY FASHION DISRUPTED
‘Dirty Fashion Disrupted’ assesses where global clothing companies and viscose producers stand in the transition towards responsible viscose. Through detailed scrutiny of 91 brands’ and retailers’ transparency and sourcing policies, and producers’ responsible production plans, the report examines the progress to date and gaps in existing commitments and pledges.
In August 2019, the Changing Markets Foundation – along with Fashion Revolution, Ethical Consumer, the Clean Clothes Campaign and WeMove.eu – reached out to over 90 global clothing brands and retailers, asking them for their most recent information on how much viscose they use, the details of any policies they have to address the environmental impacts of their viscose supply chain, the names and factories of their viscose suppliers, any plans to disclose these suppliers publicly in the future, and inviting them to commit to the Roadmap towards responsible viscose and modal fibre manufacturing.

SOME IMPROVEMENTS…
Many brands have shown a marked increase in transparency on their viscose supply chain. On their websites, four of the brands who have signed onto the campaign, Esprit, Tesco, M&S and ASOS, now publicly list the companies – down to the factory names – that provide them with viscose fibre. The remaining signatories (apart from Inditex), as well as several other brands, have disclosed the name of at least several of their viscose suppliers on their websites.
Orsola de Castro, Founder and Creative Director of Fashion Revolution commented:
“Transparency is visibility. We want to see the fashion industry, respect its producers and understand its processes. We want a clear, uninterrupted vision from origin to disposal to foster dignity, empowerment and justice for the people who make our clothes and to protect the environment we all share.”
STILL NOT ENOUGH ACTION…
The vast majority of brands are still lagging a long way behind the frontrunners on transparency. You can see which brands are taking steps towards more responsible viscose here: http://dirtyfashion.info/
Ten major high street brands and retailers have committed to take action on responsible viscose supply. However, luxury brands, including Prada, Dolce & Gabbana and Dior and low-cost retailers such as Walmart, Matalan and Boohoo, are failing to take action on polluting supply chains, devastating ecosystems and causing severe health impacts in local communities in India, China and Indonesia. It’s clear that the commonality among the laggards isn’t price point, but willingness to take fashion’s footprint seriously.
More than 25% of the brands investigated have no viscose policy in place, and many of these lack any environmental policy. Still, the Changing Markets has seen an increase in the number of brands responding to their questions and engaging with the campaign. For a full list of their findings, go here.
THE ROADMAP
In 2018, Changing Markets launched a Roadmap towards responsible viscose and modal fibre manufacturing to address the environmental and social problems in its manufacturing and provide a blueprint for responsible production for brands.
Ten major brands and retailers – Inditex, ASOS, H&M, Tesco, Marks & Spencer (M&S), Esprit, C&A, Next, New Look and Morrisons – have now made a public pledge to integrate its requirements into their sustainability policies. These brands are also expected to engage with their suppliers and use their leverage to drive towards more responsible viscose production.
Urska Trunk, Campaigns Adviser, Changing Markets Foundation commented:
“With increasing awareness of the environmental and social impacts of the fashion industry, people expect clothing companies to take responsibility for their supply chains. Brands and retailers can no longer turn a blind eye to this. They need to rise to the challenge and open their supply chains up to external scrutiny to put the industry on a more sustainable footing.”
WHAT CAN WE DO?
As citizens and consumers, we must use our voices to demand that fashion brands source materials in a transparent and responsible manner. It is unacceptable that over a quarter of the surveyed brands have turned a blind eye on viscose production that poisons people and contaminates waterways. Let’s ask #WhoMadeMyClothes? because we know that transparency is the first step in achieving a clean fashion industry that is safe for the wearers and the workers.
Tweet brands using the hashtag #dirtyfashion and ask them to be more transparent and move towards more responsible viscose here. Sign the petition to demand more responsible viscose here.
This month’s Power of Influence takes us in a bit of a different direction. On a 15 minute walk from London Euston to London Kings Cross, Fashion Revolution co-founder Orsola de Castro and renowned fashion critic and columnist Sarah Mower spoke with Sara Arnold of Extinction Rebellion (and Higher Studio) about the recent protests, the aim of the movement and the next steps in their fight for climate justice. Shortly after this interview, the UK Parliament declared a climate change emergency.
A little bit of context: On Saturday April 27th, during Fashion Revolution Week and towards the end of Extinction Rebellion’s 2 week occupation of Central London, Slow Factory hosted “Study Hall: Sustainability as a Culture”. The event (in its first international edition) was held in London, UK. Before the event, the Fashion Revolution team along with Sara Arnold, Sarah Mower, speakers, attendees and supporters took a walk to discuss the current happenings.
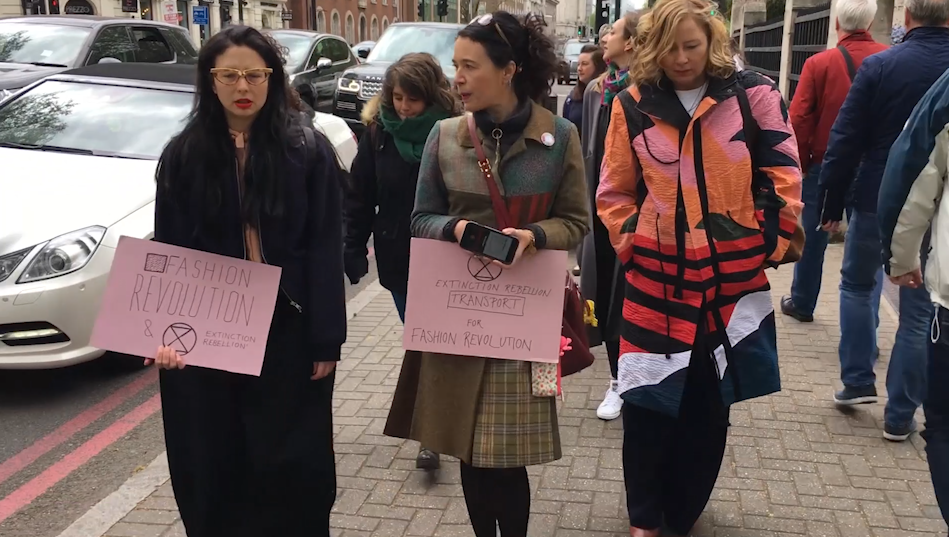
Here’s what was said:
Orsola de Castro: So the response to the protests… people are really prepared to put themselves out there. There were over 1000 arrests you say. Did you find that the overall response was positive?
SA: There has been criticism of the tactics used, there has been criticism of disruption, but that’s not we’re worried about. We want people to hear our demands, that’s what people should be focused on. I think we are making progress on that. Everyone is talking about climate change in a different way. Talking about it as an emergency. It doesn’t matter if they don’t agree with how we’ve gone about doing things. As long as it works.

OdC: I’ve found that one of the reasons why we (Fashion Revolution) wanted to do this is the symbolism of joining hands. Even if everyone has a different way of doing things. The fact that the message is one of urgency is what we want to show. We need to all join together.
Could you tell me a little about how you guys started?
SA: Yes, so Extinction Rebellion were a group called Rising Up which started, in 2016, as a group of activists who wanted to theorise how they would go about creating this social change that we needed. They researched and put into practice different tactics. A member of Extinction Rebellion, Roger Hallam, who is currently doing his PhD at King’s College on these issues, one of the things he did was engage with an activist group at King’s that for years had been trying to get the University to disinvest from fossil fuel. They decided to stage a hunger strike. They were told that this process, even just the bureaucracy of disinvesting from fossil fuels would take a year to sort out. They said ‘okay, so let’s just try it’. So they went on hunger strike.
Sarah Mower: Because the university was investing in fossil fuels?
SA: Exactly. The whole process, from start to finish, from them going on hunger strike to all the investment coming out was 2 weeks. When they were told it would take years. So it just goes to show that direct action makes change. People do what they think is not possible when they are faced with disaster.
OdC: When I went to the first extinction rebellion meeting, you were talking about in war and in emergency, people make things happen. So the factories go from producing kitchenware to producing arms. When it is a state of emergency, historically, we’ve known citizens and organisations to take action pretty rapidly.
SA: Exactly. Now we have to get this declaration through to them so they can act.

OdC: And so what about the involvement of Greta (Thunberg)?
SA: Greta was there when we held the Declaration of Rebellion on the 31st of October 2018. So we’ve had her support since the beginning. It’s really great that she came back at this time for the protests.
SM: She has changed everything.
OdC: She has changed everything.
OdC: You have other hubs in other countries, do you find there are other meaningful partnerships with local organisations in the rest of the world? Are you finding that people want to join you or do you find that they are hesitant to do so?
SA: The International Rebellion was in 33 countries. We have groups set up in 49 countries.
OdC: So like Fashion Revolution, you are de-centralised in the sense that it is volunteer run and people start their own groups.
SA: Yes. So we have 200 groups in the UK alone. The groups outside of the UK can have different demands to ours. They can adapt what we have done to respond to their own political situation. We’re so fortunate here to have police that are peaceful. And we have to use that privilege. We have a really engaged group in Ghana but if they did the same thing we are doing, they are looking at being arrested and then disappearing. It’s important for us to have solidarity with them. We keep a list of the names of those people so if anything does happen, we can protect them. It really interesting to get into that and see how we can help to take it further, internationally.
OdC: There are issues when you are a global group and you are dealing with law in different countries, even though the message is the same. Its important to recognise that.
OdC: How do you deal with citizens apathy out of fear? That people are so scared over what will happen, that they tend to go home and not know where to start.
SA: We need to really bring about this sense of urgency. That this is an absolute emergency. I feel its important to make people understand what the consequences are. We are talking about mass starvation, the death of billions of people if we reach a certain tipping point. Starvation is something we are really heading towards. We have 30 to 40 years left of fertile soil in this country, other countries are already hitting that. Let alone all the other problems. We are so dangerously close to hitting the tipping point.
Everyone is going to react to this differently. Everyone will go through a process of grief. And for a lot of people, grief will mean denial. That’s fine, you just have to feel compassion towards that. With extinction rebellion, what we are saying, is that when you give people the truth, a certain percent of the population, we think between 1 and 3% will rise up. And that is all we are aiming for. We need that 1 to 3% to rise up, to bring this to the governments and to take control.
OdC: And speak truth to power.
SA: Yes. We’ve been trying for the last 30 years to give people this positive message that we hope people will engage with and that great, but we don’t have time for that now.

SM: So what do you think when Greta Thunberg stands in front of Michael Gove and he acts all Mea culpa. How do we hold him to account and get through real change?
SA: It’s a difficult question.
SM: If we’re talking about footfalls and governmental change.
SA: This is stage 1 of the rebellion. We can rise up and be bigger next time if we need to. I think. As we are doing that, we are waking people up to this emergency and its not something you can turn the clock back on. I think sooner or later the government will have to act.
OdC: I thought Mary Creagh was very honest at the recent Fashion Question Time when she was saying that we cannot do 2025 but working towards 2050, hoping it will gradually get faster and easier.
‘We aren’t going to get to net zero by 2025. The science will tell us what to do to get to net zero by 2050, and then in five years’ time to 2040 and then we’ll aim to get there for 2035. We have wasted the last 10 years, we’ve had no new policy in this country to change behaviour and we’ve done some policy mistakes along the way.’ Mary Creagh, Fashion Question Time at the V&A
SA: I think that we have to hit 2025. The Arctic is melting. We could lose it in a few years. That could be the tipping point that takes us into oblivion. We have to set our targets at something that seems impossible because then we are forced to look at system change. It is not about what we can do within the existing system, we have to look beyond that and listen to the science.

OdC: The science…the science corroborates that if we did stop now, it would get worse before it gets better.
SA: That’s the thing, pollution is currently cooling the earth. We are now 1.1 degrees warmer than we were during pre-industrial times. We need to keep ourselves below 1.5 if we are to avoid the most catastrophic consequences. BUT..If we slam on the brakes right now, the pollution will clear, causing an abrupt rise in temperature. This increase has been predicted to be between 0.5 and 1.1 degrees and so we may well have already used the carbon budget associated with 1.5 degrees of global heating. And that also puts us dangerously close to tipping points that will lead us into a so called ‘hot-house earth pathway’ of runaway climate breakdown. Its predicted that we reach this tipping point at around 2 degrees of global heating. Prof. Jem Bendell released a paper, ‘Deep Adaptation’, that puts together all the science to conclude where it is we are headed. His conclusion is that the collapse of civilisation is soon and inevitable. That immense catastrophe is likely and extinction possible.
‘I have chosen to interpret the information as indicating inevitable collapse, probable catastrophe and possible extinction.’ – Prof. Jem Bendell, Deep Adaptation: A Map for Navigating Climate Tragedy
So that is why we have to think about how we are going to adapt our culture, how we can reconnect with the thought of what it means to have a fulfilled life. What is important to us? This is why we say it’s not really about providing hope to people its saying we just need the courage to get through this and do what is necessary.
OdC: If we look at precedence, historically, the last time there was a massive mobilisation was in the 60’s. I often joke that the peace sign embroidered on jeans practically stopped the Vietnam war but it essentially sparked consumerism.
SM: Its true and now that generation, who are now grandparents, see their grandchildren protesting against it. It’s something I find very moving.
Further reading:
BBC: UK Parliament declares climate change emergency
Fashion Revolution Blog: Fashion Question Time at the V&A
The Guardian: Human society under urgent threat from loss of Earth’s natural life
Open Democracy: Britain just declared a climate emergency. What happens next?
IPCC: Special Report: Global Warming of 1.5 ºC
Life Worth: Deep Adaptation: A Map for Navigating Climate Tragedy
The Library: Study Hall: London Central Saint Martins
Check back every month for more in the Power of Influence series. We’ll post a new entry on the last day of each month throughout 2019. If you think there is someone we should be talking to, drop us a line on instagram.
We host Fashion Revolution Week in April of every year. This year kicked off on the 22nd of April. Throughout the week we encouraged people to ask brands ‘who made my clothes’ in hopes of shining a light on the unknowns of the fashion industry. By doing this, we hope to shift the focus from consumers to brands, and to all the hands involved, be it producers, workers, farmers or otherwise. We track the reach and impact of collaborators throughout Fashion Revolution Week and use the findings to fight for change worldwide, through government and policy. We are able to do this through the generous support of people like you. Please consider donating. Thank you.
Tomorrowland: how innovation and sustainability will change the fashion panorama.
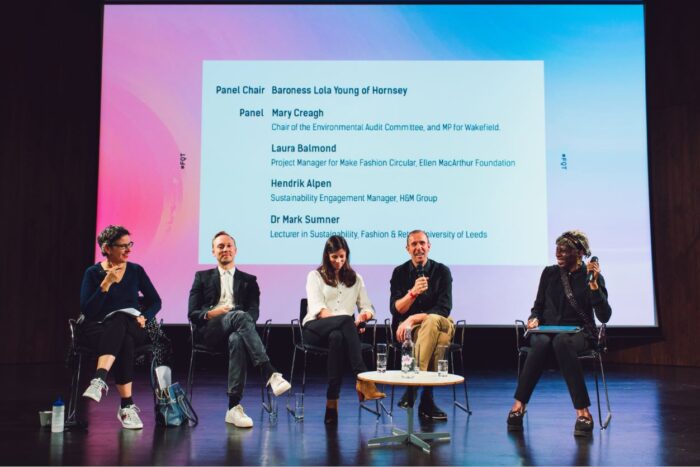
On Wednesday, 24th April 2019, Fashion Revolution hosted our fifth annual Fashion Question Time, a powerful platform to debate the future of the fashion industry during Fashion Revolution Week. This year Fashion Question Time was hosted for the first time at the V&A museum and opening the event up to the public for the first time. The theme this year was Tomorrowland: how innovation and sustainability will change the fashion panorama.
Chaired by Baroness Lola Young of Hornsey, this year’s panel brought together leading figures across government and the fashion industry to discuss the future of the fashion industry.
Attendees included high-level fashion industry representatives from across the sector, global brands, retailers, press, MPs, influencers, and NGOs. Panelists included Mary Creagh, MP and Chair of the Environmental Audit Committee; Laura Balmond, Project Manager, Ellen MacArthur Foundation; Mark Sumner, Lecturer in Sustainability, Fashion & Retail, University of Leeds, and Hendrik Alpen, Sustainability Engagement Manager, H&M Group.
After a welcoming speech from Tim Peeve, an opening speech was made by Sarah Ditty, Policy Director for Fashion Revolution:
“There is an ocean of truth lying undiscovered before us when it comes to the fashion industry of tomorrow. We urgently need to focus on innovation and we need sustainability to be scaled up.”
Below we have selected some questions and answers that were discussed over the 1 hour ½ debate during Fashion Question Time 2019 at the V&A:
Olivia Shaw, Campaign Support Officer for #LoveNotLand
fill and London Waste & Recycling Board asked:
“In a world with finite resources, why does the fashion industry waste around three quarters of what it creates and how are we going change this model to create a fair system for all?”
Laura Balmond, Project Manager, Ellen MacArthur Foundation: It’s not possible to continue as we go on… The amount of clothes produced is rapidly increasing – and we are using clothes 40% less. Less than 1% of materials are going back into fashion we make… We need a huge systemic rethink .. I believe that the circular economy will be business-led. We need businesses to get behind this common vision… The current system doesn’t work. The leaders will continue to push ahead – will the others exist in 5 years time?
Mark Sumner, Lecturer in Sustainability, Fashion & Retail, University of Leeds: Technically there are lots of solutions but there’s no motivation… We have the opportunity to change this and legislation plays an important role. The fashion industry has been around for thousands of years. It plays an important role in self-esteem and identity, plays an important part in our lives. But we can’t stick with the model we have at the moment, we need to change. The Modern Slavery Bill is a good starting point but we need more legislation. More innovative structures in place to penalise businesses – the responsibility needs to be across the whole system.
Mary Creagh, MP and Chair of the Environmental Audit Committee: The current fashion industry model promotes over consumption and under utilisation. My concern is that the policy space in this country, which has historically been a leader on these issues, has been crowded out by the Brexit psychodrama and the space for creative and necessary responses to this is being handed to us. We’re in a unique situation where the public is dragging the Government. We debated the environment twice in Parliament twice yesterday so things are changing but we all need to think about our overconsumption… We also need to strengthen regulation to require greater executive level accountability for tackling modern slavery and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in business and supply chains.
Hendrik Alpen, Sustainability Engagement Manager, H&M Group: Moving to a circular model makes business sense. Right now, H&M operates one of the biggest global take-back schemes.
Sarah Ditty, Fashion Revolution, Policy Director on behalf of Labour behind the Label asked:
The one safety initiative that came out of the Rana Plaza collapse, the Accord on Fire and Building Safety in Bangladesh, is at risk of being expelled from the country at the moment, putting all the progress made in the last six years at risk. At the moment over 50% of the factories still lack adequate fire alarm and detection systems and 40% are still completing structural renovations, these life-saving remediations need to be overseen by the Accord. With the Accord under threat, how can innovations in transparency create a better future for garment workers?
Laura Balmond, Project Manager, Ellen MacArthur Foundation: With innovations around transparency, relies purely on the information that is inputted at the very beginning. So, this then raises the question of how do we verify that and how do we ensure the information you are receiving is correct? Therefore, what are the financial incentives to improve the system? We must incentivise accurate data inputting.
Hendrik Alpen, Sustainability Engagement Manager, H&M Group: The Accord is a very well working mechanism. So, we as a brand, and other brands hope it will continue. Last year 98% of our suppliers were compliant with the Accord’s requirements, and this year, it will be 100% compliance. You talk about incentives, so that’s a sort of incentive we can create to get something back for the work we are investing, besides, you know, it’s the right thing to do. This can also create a level playing field between brands and this is very crucial to make informed choices.
Mary Creagh, MP and Chair of the Environmental Audit Committee:
The real costs of what goes into those clothes are not truly priced. We will only have change if we price clothing based on the material, the labour, and carbon emissions. Those costs are currently passed onto the countries of production… Currently, it’s down to little NGOs to police big brands. Footlocker doesn’t provide an anti-slavery statement on their website, for example… We must make accountants and CEOs accountable for slavery and emissions. Anyone with a pension fund can buy shares in a business, and as a shareholder, you can go to AGMs and to put pressure on these brands.
Sara Arnold of Extinction Rebellion asked:
To have a chance of avoiding the worst effects of the climate and ecological collapse, we must get to net zero carbon by 2025 and halt the loss of biodiversity. The mobilisation we need is unprecedented and as an industry, we should be declaring climate and ecological emergency and acting as so. If this was treated as the emergency that it is, would there be any place for fast fashion? Would there be a place for fashion at all?
Hendrik Alpen, Sustainability Engagement Manager, H&M Group: Obviously, it is hard to say we shouldn’t exist! But I can relate to the thoughts. So, our job is to reduce the impact of what we do. So that’s why we set the goal to be climate positive by 2040, that may be too late, but we are discussing timelines. We have made changes across our stores, and office to be powered by renewable electricity. So, the challenge we have is how do we bring that into the supply chain? And our first goal is to have a climate neutral supply chain by 2030. That’s a huge challenge, we don’t know how to do that, but that’s the challenge we are taking on and we have to take on. Then the question is how can we continue to operate with such a business model which still brings fashion to the people but how do we do that in a better way? Our business model is based on selling products and it still will be for a while and on the other hand, that means jobs for people, joy for people but we need to find a different way.
Laura Balmond, Project Manager, Ellen MacArthur Foundation:
Think of the global population, what do people want, what do people need. Firstly, we need clothes, but then we have a prospect of fashion. Fashion is creative and meets a variety of needs of the people. So you’ve got on the one hand, Instagram bloggers who wear many different outfits and that’s how they’ve learnt to operate. And that’s okay, we don’t want to stifle creativity or fun. At the opposite end of the spectrum, you’ve got the guy that’s had his pair of Levi’s and loves them and doesn’t want them to ever wear out and he’s set for life. So how can the fashion industry rise to the challenge of meeting both these needs and still continue to exist? This can lead to interesting things coming out of this, for instance, an organisation that curates a digital wardrobe, so why do they necessarily need to own clothes at all…This is the end where rental models, swapping will be the way to keep clothes in use for as long as possible, just not with the same person. Then, on the other hand, we need to create well made, durable and repairable clothing. And that’s the challenge for the fashion industry: how can it rise to better meet the needs of the consumers?
Mark Sumner, Lecturer in Sustainability, Fashion & Retail, University of Leeds:
We’ve got 11 years to solve climate change, and I suspect it’s going to be less than that. So I agree, that it’s not fast enough. But I think you need to understand that its systemic part of culture and the part that the fashion industry plays in it. Fashion plays a really important role in our lives, for self-esteem, identity, it’s about projecting our position in society. It a really important part of our lives… I think it’s really interesting when people talk about fast and slow fashion, I go around fabric mills and garment factories, you can see excellent best practice happening in fast fashion supply chain and at the same time, around the corner you see absolutely diabolical conditions in factories supplying to luxury brands, sometimes run by the mafia. So, to think that luxury, fast fashion and slow fashion are different concepts is false. I think what we need to be looking at is brands and retailers that are doing good things, H&M, for example, are trying lots of different models, they haven’t got the answers yet but at least they are trying. Some brands out there don’t even know they have to ask the question about climate change, it’s not on their agenda at all. Those organisations are the ones we really need to metaphorically give them a kick. Different business models need to be developed but that does require significant change, so it’s also about changing the way we behave.
Mary Creagh, MP and Chair of the Environmental Audit Committee:
Thank you [to Extinction Rebellion] for creating the operating space for MP’s like me, who have always been a bit of a lonely voice, to become normalised.
But also, while there is a climate emergency, there’s also a social emergency on hand. And we need to tackle both of these things together. And switching to a low-carbon economy, we have to make it adjust transitionally, we have to make sure we don’t create winners and losers, so that fashion shouldn’t just become something for rich people to enjoy. So, when we look at how we are going to transition, we have got problems with our transport, in agriculture and the way we fuel our homes. So those are the three policy challenges for government. Had we moved from our over-consuming society very quickly, we aren’t going to get to net zero by 2025. The science will tell us what to do to get to net zero by 2050, and then in five years’ time to 2040 and then we’ll aim to get there for 2035. We have wasted the last 10 years, we’ve had no new policy in this country to change behaviour and we’ve done some policy mistakes along the way. I think fashion needs to set out it’s roadmap to net zero. It needs to say how we get to net zero and the target needs to be legally enforceable and not just voluntary.
Dr Mark Sumner, Lecturer in Sustainability, Fashion & Retail, University of Leeds:
This isn’t just about fashion, it’s a culture of consumption. There are brands doing good stuff who are being lambasted by the press and the ones that aren’t doing anything are slipping into the shadows.
Closing Fashion Question Time 2019, Orsola de Castro, co-founder of Fashion Revolution, made a powerful closing speech:
“There is absolutely no excuse anymore. We all have to do what is required of us as people, people working in companies, in governments, in education, in the media, and at home. We have to fight the system and we have to fight our lifestyle. We can’t do this without information and we can’t access verifiable, comparable and understandable information without transparency and public disclosure… We have to move from a culture of exploitation to one of appreciation and place respect for resources and for each other before every deed and every process.”
The other questions asked were:
Antonio Roade, Senior CSR Manager, New Look asked:
Technology will be vital to transition towards a circular economy; and we keep on seeing big companies investing millions collaborating with different research institutions; in different areas and often with no clear outputs. How do we coordinate different initiatives and who should be taking the lead on this (research institutions, governments or brands)?
Elle L, Artist, Expert Advisor in Fashion and Media to United Nations Environment Programme asked:
As we know, fast fashion uses a lot of synthetics which we in the room and the government now know to be highly toxic and damaging to the environment — do you think that a tax can and should be implemented to minimise or how do we phase out the amount of synthetics produced?
Julie Hill, Chair of WRAP asked:
What are the best tools to drive resource efficiency and transparency in the fashion supply chain?
Jennifer Eweh, Designer and Entrepreneur, Eden Diodati asked:
What are the opportunities and challenges involved with automation, blockchain, and artificial intelligence being used within the fashion supply chain?
Siobhan Wilson, Owner, The Fair Shop asked:
Small business and organisations have been driving change in communities across the country and beyond in making, repairing, reinventing and reusing. How can these businesses be nurtured and supported more here in the UK, so they can flourish at a greater scale and gain further exposure to a mainstream fashion audience?
Jasmine Hemsley, Cook, Author and wellness expert, asked:
What will our future look like without sustainable fashion being commonplace?
A very special thank you to the Edwina Ehrman for opening the V&A to Fashion Revolution’s Fashion Question Time and to the rest of the V&A team for your efforts in making this event a success. And a thank you to Sienna Somers and the rest of the Fashion Revolution team for organising this event.
All images Copyright Rachel Manns / www.rachelmanns.com / @rachel_manns / Rachel Manns is an internationally commissioned freelance photographer based in London, UK. She has spent the last decade shooting for a range of clients all over the world. She has a strong passion for sustainability and human rights. With fierce ethical values and a beautiful visual style, Rachel’s work perfectly intertwines the two. Her aim is to use her camera to aid positive change globally, whether that’s politically or commercially, whilst never compromising on aesthetic. Get in contact for rates.
WHY SHOULD BRANDS PUBLISH SUPPLIER LISTS?

Publicly disclosed supplier lists are helping trade unions and workers rights organisations to address and fix problems which workers are facing in the factories that supply major brands and retailers. This sort of transparency makes it easier for the relevant parties to understand what went wrong, who is responsible and how to fix it. It also helps consumers better understand #whomademyclothes.
“Knowing the names of major buyers from factories gives workers and their unions a stronger leverage, crucial for a timely solution when resolving conflicts, whether it be refusal to recognise the union, or unlawful sackings for demanding their rights. It also provides the possibility to create a link from the worker back to the customer and possibly media to bring attention to their issues.” says Jenny Holdcroft, the Assistant General Secretary of IndustriALL Global Union
HAVE WE SEEN AN INCREASE IN BRANDS PUBLISHING SUPPLIER LISTS?

Since we began the Fashion Transparency Index in 2016, we have seen a significant increase in the number of brands publishing their first tier, processing and raw materials suppliers. In our 2020 edition of the Fashion Transparency Index, 101 out of 250 brands (40%) are publishing their first-tier manufacturers, up from 35% in 2019. These are the facilities that do the cutting, sewing and finishing of garments in the final stages of production.
60 out of 250 brands (24%) are publishing some of their processing facilities, up from 19% in 2019. These are the sorts of facilities that do ginning and spinning of yarn, knitting and weaving of fabrics, dyeing and wet processing, leather tanneries, embroidering and embellishing, fabric finishing, dyeing and printing and laundering.
And, 18 out of 250 brands (7%) are publishing some of their raw material suppliers, up from 5% in 2019. These suppliers are those that provide brands and their manufacturers further down the chain with raw materials such as cotton, wool, viscose, hides, rubber and metals.
HOW MANY BRANDS ARE NOW PUBLISHING SUPPLIER LISTS?
We have looked at large brands (over £36 million annual turnover) beyond the Fashion Transparency Index to count the number that are publishing lists of their suppliers. Below, you will find a list of over 200 brands that are publishing their first-tier manufacturers, 60 brands that are publishing their processing facilities and 21 brands that are publishing their raw material suppliers.
We are always pushing brands to provide more information about the people who make their clothes, and you can encourage them to do so too. Always ask the brands you buy #WhoMadeMyClothes. You can do this by tagging your favourite brands on social media and using this hashtag, or you can use our automated email tool to get in touch with them directly.
Brands who publish first-tier supplier lists
First-tier/ Tier One/ manufacturing suppliers are those which have a direct relationship with buyer e.g. production units, Cut Make Trim (CMT) facilities, garment sewing, garment finishing, full package production and packaging and storage.
& Other Stories (H&M group)
Abercrombie & Fitch
Adidas
ALDI-Nord
ALDI SOUTH
Amazon
Ann Taylor
Anthropologie (URBN)
ARROW (PVH)
ASICS
Aldi North
ASOS
Athleta (GAP Inc.)
Autograph (Speciality Fashion Group)
Banana Republic (GAP Inc.)
Berghaus (Pentland Brands)
Berlei (Hanes)
BESTSELLER
BigW (Woolsworth Group)
Black Pepper (PAS Group)
Boden
Bon Prix
Bonds (Hanes)
Boxfresh (Pentland Brands)
Brand Collective
Brooks Sports
Burton (Arcadia)
C&A
Calvin Klein (PVH)
Champion (Hanes)
Cheap Monday (H&M group)
City Chic (Speciality Fashion Group)
Clarks
Cole’s (Wesfarmers Group)
Columbia Sportswear Co.
Converse (NIKE, Inc)
Cos (H&M group)
Cotton:On
Crossroads (Speciality Fashion Group)
Curvation (Fruit of the Loom, Inc.)
David Jones
Debenhams
Designworks (PAS Group)
Disney
Dorothy Perkins (Arcadia)
Dressmann (Varner)
Eagle Creek (VF Corporation)
Eastpak (VF Corporation)
Eileen Fisher
El Corte Inglés
Ellesse (Pentland Brands)
Esprit
Evans (Arcadia)
Factorie (Cotton On Group)
Fanatics
Fjällräven
Forever New
Free People (URBN)
Fruit of the Loom
G-Star
Galeria Inno (HBC)
Galeria Kaufhof (HBC)
Gap
George at Asda (Walmart)
Gildan
H&M
Hanes
Helly Hansen
HEMA
Hermès
Holeproof Explorer (Hanes)
Hollister Co. (Abercrombie and Fitch Co.)
Hudson’s Bay Company (HBC)
HUGO BOSS
Hurley (NIKE, Inc)
Intermix (GAP Inc.)
IZOD (PVH)
JACK&JONES (BESTSELLER)
Jack Wolfskin
Jacqueline de Yong (BESTSELLER)
JAG (APG & Co)
Jansport (VF Corporation)
Jeanswest
JETS Swimwear (PAS Group)
Jockey (Hanes)
John Lewis
Joe Fresh (Loblaw Companies Limited)
Jordan (NIKE, Inc)
Junarose (BESTSELLER)
KangaROOS (Pentland Brands)
Kathmandu
Katies (Speciality Fashion Group)
Kaufland
Kayser (Hanes)
Kipling (VF Corporation)
Kmart Australia (Wesfarmers Group)
Lacoste
Lee (VF Corporation)
Levi Strauss & Co.
Lidl
Lindex
Littlewoods (Shop Direct)
Loblaw
Loft (Ascena)
Lord & Taylor (HBC)
lucy (VF Corporation)
Lululemon
Majestic (VF Corporation)
Mamalicious (BESTSELLER)
Mammut
Marco Polo (PAS Group)
Marimekko
Marks & Spencer
Matalan
MEC
Millers (Speciality Fashion Group)
Missguided
Miss Selfridge (Arcadia)
Mizuno
Monki (H&M group)
Monsoon
Morrisons (Nutmeg)
Name It (BESTSELLER)
Napapijiri (VF Corporation)
Nautica (VF Corporation)
New Balance
New Look
Next
Nike
Noisy May (BESTSELLER)
Nudie Jeans
Old Navy (GAP Inc.)
Only (BESTSELLER)
Only & Sons (BESTSELLER)
Outerknown (Kering Group)
Outfit (Arcadia)
OVS
Patagonia
Pieces (BESTSELLER)
Pimkie
Playtex (Hanes)
Primark
Prisma (S Group)
Puma
R.M Williams
Razzamatazz (Hanes)
Red or Dead (Pentland Brands)
Reebok (Adidas Group)
Reef (VF Corporation)
REI Co-op
Review (PAS Group)
Rider’s by Lee (VF Corporation)
Rio (Hanes)
River Island
Rivers (Speciality Fashion Group)
Rock & Republic (VF Corporation)
rubi (Cotton On Group)
Russell Athletic (Fruit of the Loom, Inc.)
Sainsbury’s – Tu Clothing
Saba (APG & Co.)
Sak’s Fifth Avenue (HBC)
Selected (BESTSELLER)
Sheer Relief (Hanes)
Sisley (Benetton Group)
Smartwool (VF Corporation)
SPALDING (Fruit of the Loom, Inc.)
Speedo (Pentland Brands)
Sportscraft (APG & Co.)
Supré (Cotton On Group)
Target
Target Australia (Wesfarmers Group)
Tchibo
Ted Baker
Tesco
The North Face (VF Corporation)
The Warehouse
Timberland (VF Corporation)
Tod’s
Tommy Hilfiger (PVH)
Tom Tailor
Topman (Arcadia)
Topshop (Arcadia)
Under Armour
Uniqlo (Fast Retailing)
United Colours of Benetton (Benetton Group)
Urban Outfitters (URBN)
Van Heusen (PVH)
Vanity Fair Lingerie (Fruit of the Loom, Inc.)
Vans (VF Corporation)
Vassarette (Hanes)
Vero Moda (BESTSELLER)
Very (Shop Direct)
Victoria’s Secret (L Brands)
Vila Clothes (BESTSELLER)
Voodoo (Hanes)
Wallis (Arcadia)
Warner’s (PVH)
Weekday (H&M group)
White Runway (PAS Group)
Wrangler (VF Corporation)
Yarra Trail (PAS Group)
Y.A.S. (BESTSELLER)
Zalando
Zeeman
Total: 204
Brands who publish processing facilities list
Processing facilities (often referred to as facilities beyond tier 1) are involved in the production of clothing whose activities could involve ginning and spinning, knitting, weaving, dyeing and wet processing, tanneries, embroidering, printing, fabric finishing, dye-houses and laundries.
Adidas
Anthropologie (URBN)
ASICS
ASOS
Banana Republic (GAP Inc.)
Bon Prix
Burton (Arcadia)
C&A
Calvin Klein (PVH)
Champion (Hanes)
Clarks
Converse (NIKE, Inc)
Debenhams
Disney
Dressmann (Varner)
Eileen Fisher
Ermenegildo Zegna
Esprit
Free People (URBN)
Gap
Gildan
G-Star RAW
H&M
Hanes
Helly Hansen
HEMA
Hermès
Jack Wolfskin
Jordan (NIKE, Inc)
Kaufland
Levi Strauss & Co.
Lindex
Lululemon
Monsoon
New Balance
New Look
Nike (Nike, Inc.)
Nudie Jeans
Old Navy (GAP Inc.)
Patagonia
Puma
Reebok (Adidas Group)
Russell Athletic (Fruit of the Loom, Inc.)
Sainsbury’s – Tu Clothing
Target
Tchibo
Tesco
The North Face (VF Corporation)
The Warehouse
Timberland (VF Corporation)
Tommy Hilfiger (PVH)
Topman (Arcadia)
Topshop (Arcadia)
Uniqlo (Fast Retailing)
United Colours of Benetton (Benetton Group)
Urban Outfitters (URBN)
Van Heusen (PVH)
Vans (VF Corporation)
Warner’s (PVH)
Wrangler (VF Corporation)
Total: 60
Brands who publish raw materials supplier list
Raw material suppliers are those which provide the commodity for the production of clothing e.g. cotton, wool, viscose or polyester.
ASOS
Balenciaga (Kering)
Bottega Veneta (Kering)
C&A
Eileen Fisher
Ermenegildo Zegna
Esprit
Gucci (Kering)
H&M Group
Lululemon
Marks & Spencer
Morrisons (Nutmeg)
Nudie Jeans
Patagonia
SAINT LAURENT (Kering)
Tesco
The North Face (VF Corporation)
Timberland (VF Corporation)
United Colours of Benetton (Benetton Group)
Vans (VF Corporation)
Wrangler (VF Corporation)
Total: 21
Please note: We are not endorsing the brands included in this list; this is not a ‘seal of approval.’ While publishing supplier lists is a necessary step towards greater transparency and improved conditions in fashion supply chains, it does not guarantee ethical business practices. However, we hope you find this list informative and continue to ask brands #whomademyclothes.
This list is not exhaustive and only accurate as of April 2020; if you are aware of other large brands (over £36 million annual turnover) that are publishing their suppliers, please let our Policy and Research team know at transparency@
Sparked by the buzz around HRH Meghan Markle choosing to shop amongst sustainable brands (yay), we found ourselves interested in learning more about the conscious and subconscious effect of social influencers and how that can shape our buying habits. Throughout 2019, we will be sharing our ‘Power of Influence’ series, talking to people within the fashion and social media realms about how they are using their platform for positive action. In this post, we celebrate Mutha.
Mutha are my favourite new source for all things sustainability. They not only have great fashion related content but they also delve in to other areas such as food, tech, sport and feminism. Their youtube channel is hosted by an insanely engaging team of presenters and their #relatable language and design aesthetic is something to be envious of. Current faves in their playlists include ‘Zero Waste Man‘ and ‘Black Friday Madness‘. To find out more about how it all happens, I chatted to Susan Adegboye, Mutha’s social media coordinator.
[youtube v=”6XqRPsULEnk”]
What is Mutha and how did it start?
So Mutha stemmed from wanting to celebrate the individuals and organisations operating in the world of food, fashion, travel and sport that are making a conscious effort to look after this planet of ours. We wanted to create a platform dedicated to the forward thinkers that were shifting the dial for a sustainable future, highlighting the importance of looking after the planet but without the scaremonger tactics.
Can you explain a little about the kind of content Mutha is creating to bridge that gap?
We tried to bridge that gap by including communities and groups that have previously never really been involved. A good example of this is SpAir Max Day, where we decided to tap into the sneaker community.
Coinciding with Nike Air Max Day on March 26th, we filmed a two-part series with renowned sneaker head Kish Kash, encouraging the sneaker community and a few household names such as Annie Mac, Clara Amfo and Leo Greenslade, to look into their vaults and donate some of their used, worn-in and probably landfill destined kicks to launch the first ever pop up sneaker shop where customers donate instead of buy. With the aim of collecting 1000 pairs of Air Max, cleaned by the team at Jason Markk and donated to the Brixton Soup Kitchen clothing and shoe bank.
We wanted to show the Mutha audience that upcycling and donating our used clothing and shoes not only has a positive impact on the environment, but that it can help people in our community in need. We wanted to work with the sneaker community to show how they can come together to do something good.
[youtube v=”ABaUzcJk33Q”]
I think thats a really interesting point – including communities that haven’t previously been part of the conversation. At this point, it feels like there is something everyone can do to play their part.
Exactly!
One of Muthas instagram post states ‘you don’t have to be perfect, just do your best’. Do you think there is a tendency to shame when it comes to issues of sustainability?
Nobody’s perfect and we all make mistakes, we’re human after all. It’s about what we do after the mistakes that really matters.
On that note, the team of presenters on Mutha feels very natural, honest, like they are part of the communities they interact with and they are experiencing the challenges and issues at the same time the audience are. Was it a conscious decision to work in this way?
Our presenters and the rest of the Mutha team, do not want to preach, but rather learn and share to inspire positive change. They represent the team behind the scenes who create the content and more importantly the audience who watch it. Our presenters come from varied backgrounds and have passions in totally different areas, but are all connected in the quest to learn and to live in a more sustainable way.
Thats definitely something that personally resonated with me when I first came across Mutha. It’s an inviting atmosphere. You sympathise and relate to the faces and voices you see and hear. Have you seen a positive reaction to this approach? Do your audience get it? Are they realising what they can do?
Ah we’re happy to hear that! At Mutha we believe that change has to start from within, we’re all on a journey here and in the 9 months since we started it we’ve all seen changes in ourselves and in our habits. The world of sustainability is often filled with doom and gloom, but a lot of us feel more optimistic now than we did before we started this journey. All the people that we’ve featured on our channel (and most of the feedback that we’ve received from our audience) is that Mutha feels like a celebration and inspires us to take the small actions that lead to big change.
So what does the future of Mutha look like?
The future of Mutha looks bigger and better, creating a lasting impact on an even wider scale. We hope that we can continue to provide a place where people can learn about sustainability and appreciating the world that we live in.
Thanks, Susan!
To keep up to date with all things Mutha, you can follow them on instagram and subscribe to their youtube channel. The second part of their two part SpAir Max Day initiative launched April 4th – see the video here.
Check back every month for more in the Power of Influence series. We’ll post a new entry on the last day of each month throughout 2019. If you think there is someone we should be talking to, drop us a line on instagram.
We host Fashion Revolution Week in April of every year. This year kicks off on the 22nd of April. Throughout the week we encourage people to ask brands ‘who made my clothes’ in hopes of shining a light on the unknowns of the fashion industry. By doing this, we hope to shift the focus from consumers to brands, and to all the hands involved, be it producers, workers, farmers or otherwise. We track the reach and impact of collaborators throughout Fashion Revolution Week and use the findings to fight for change worldwide, through government and policy. We would hugely appreciate it if you would be willing to share a story or celebrate a brand you love or simply ask #whomademyclothes during Fashion Revolution Week in 2019.
Sparked by the buzz around HRH Megan Markle choosing to shop amongst sustainable brands (yay), we found ourselves interested in learning more about the conscious and subconscious effect of social influencers and how that can shape our buying habits. Throughout 2019, we will be sharing our ‘Power of Influence’ series, talking to people within the fashion and social media realms about how they are using their platform for positive action. In this post, we talk to Ashley AKA bestdressed.
There is something different about Ashley’s videos. There is no big agenda, no preaching or bragging, no shaming when she talks about clothes. There is just this subtle little undercurrent of care and attention in the way she approaches her wardrobe. Thrifting, flipping (making new things out of old things) and the occasional scattering of self-deprecating humour makes for some exceedingly entertaining videos. Being an avid fixer and flipper myself, I wondered what made Ashley start working in this way and what effect, if any, she thinks it has on her audience.
Could you share your name and various media handles:
Ashley (aka bestdressed)
Youtube: bestdressed
Instagram: @best.dressed
Upon first glance, your youtube channel might seem like many others – OOTDs, clothing hauls and ‘day in the life of’s. When digging in though, your approach to sustainability through thrifting, upcycling and flipping your finds is totally ingrained into everything you do and say. For us, this is such an important and positive message to be spreading, something that others on the platform can seem to ignore. What made you start working in this way? Was sustainable fashion something you’ve always been conscious of?
I’m flattered, but honestly I never made a conscious choice to be a ~hero~ of sustainability! My love of thrifting and tendency to rewear clothes really comes from a financial perspective. When I was a younger, I never liked thrifting, My sister would always find gems, but I’d get bored and frustrated 15 ugly sweaters in and go play Doodle Jump in a corner. But two summers ago, when was in full on chipmunk mode post-wisdom teeth removal, I needed something to pass the time before my cheeks deflated. Lo and behold, I decided to go thrifting, and finally found some cool stuff. From that point on, I was obsessed – mostly because at that point I was still working for $8 an hour at an ice cream shop and could use the cheapest clothes I could get. Plus, I was about a year into my (vastly unsuccessful at that point) YouTube career. I would post a haul or OOTW here and there, but I could never seem to keep up with other girls who would have five completely new outfits each week. Thrifting, for me, was a way to experiment with my style and make interesting content, and rewearing clothes for years (even “fast fashion” clothes from Forever21) was just a product of not having that much money.
In a lot of your videos you alter, adjust, flip your existing clothes (or second hand clothes) into something totally new. Do you think it’s something everyone could and should be doing? Does this satisfy the itch to own something new, without playing into the fast-fashion world?
For me, it’s even better! It’s like Marx’s theory of alienation from the work product, right? There’s something so satisfying about making or altering something yourself. Every time you look at it or wear it you get to be like “Damn! I did that! And nobody else has anything like it!” I know everyone’s not the craftiest or has time to alter their clothes, but I hope I can encourage people to at least give it a try! Something as simple as patching up a hole instead of throwing a shirt out, or cropping an old t-shirt are a great place to start!
Do you feel the pressure from brands to buy? Do you think it’s possible to stay fashionable without buying in excess?
Absolutely. That’s the whole job of the marketing industry. And now social media is overtaken by the marketing industry. So every day, tons of images and videos are telling you that you want new things. Honestly I fall victim to this too. It’s usually only when I’m bored or procrastinating or feeling shitty, but I’ll go into this fervor of opening tabs and adding items to my cart. Normally the total price at checkout stops me though, haha. I don’t go to malls anymore because they make me crazy. Literally my brain just goes: clothes! clothes! more clothes! I sound insane but I swear this probably happens to a lot of us. Luckily, a lot of what’s “fashionable,” at least for a certain segment of internet hipsters, is shifting towards thrifted and vintage clothes. I love that it’s cool now to wear an old oversize t-shirt or a vintage linen dress. Since my entire job revolves around fashion, I do still buy new clothes, but I always think about my purchases thoughtfully and try to mix in thrifted, vintage, sustainable, and altered clothes.
Do you see an uptake in responsibility from your followers when you share content that focuses on sustainable issues? Do their responses show that they’re thinking differently about what they buy and how they buy?
Honestly unfortunately I think it’s a bit of singing to the choir when it comes to sustainable vs. fast fashion. There are still crazy amounts of $300, $500, $5000 Wish/Zaful/Shein hauls online, with audiences willing to watch. I’m chillin over here in my corner of the internet with gals who already love thrifting. And who’s reading this article? Surely people who already care about sustainable fashion. Perhaps that’s just me being a bit of a pessimist. In the long run, I think sustainable content can change how people think, but it takes time. I hope that at least some people who have subscribed to my channel from a fashion video have found their way to a thrift haul, and after watching a couple, have tried thrifting on their own! And maybe my thrift flips makes fellow sewing nerds like me feel a little cooler lol.
Okay now for some quick ones…
- Current favourite piece in your closet?
A sherpa jacket I thrifted from the men’s section! So cozy and looks like it cost a fortune - Do you remember the first piece of clothing that you ever bought for yourself?
A gray American Eagle hoodie in 6th grade - Do you still have it?
I wore it nearly every day to school for 3 years (I was one of those kids) but we had to part ways after it was pretty much falling apart. - Do you know who made the clothes you are currently wearing?
My top is thrifted (so not sure who made it originally) and my jeans are Redone vintage Levi’s made in the US. - Top tip for others wishing to shop more responsibly?
Start with browsing a vintage or thrift store, finding a few quality sustainable pieces to invest in, looking through your own closet to find old gems you forgot you loved… or even remembering to return items you don’t end up loving – that’s a huge one! It’s so easy, you get your money back, and you don’t end up with clothing sitting in the back of your closet. You’d be amazed by how many people buy stuff and can’t be bothered to return it. I think sustainable culture can be a bit intimidating and make you feel guilty for your past purchases or if you aren’t perfectly sustainable at the start. It’s all about starting small – even if you just stop and think about one fast fashion purchase per month, that’s still awesome!
Thanks, Ashley 🙂
Check back every month for more in the Power of Influence series. We’ll post a new entry on the last day of each month throughout 2019. If you think there is someone we should be talking to, drop us a line on instagram.
We host Fashion Revolution Week in April of every year. This year kicks off on the 22nd of April. Throughout the week we encourage people to ask brands ‘who made my clothes’ in hopes of shining a light on the unknowns of the fashion industry. By doing this, we hope to shift the focus from consumers to brands, and to all the hands involved, be it producers, workers, farmers or otherwise. We track the reach and impact of collaborators throughout Fashion Revolution Week and use the findings to fight for change worldwide, through government and policy. We would hugely appreciate it if you would be willing to share a story or celebrate a brand you love or simply ask #whomademyclothes during Fashion Revolution Week in 2019.
Sparked by the buzz around HRH Megan Markle choosing to shop amongst sustainable brands (yay), we found ourselves interested in learning more about the conscious and subconscious effect of social influencers and how that can shape our buying habits. Throughout 2019, we will be sharing our ‘Power of Influence’ series, talking to people within the fashion and social media realms about how they are using their platform for positive action. First up is Arden Rose.
I was recommended Arden’s youtube channel by Youtube itself (thanks algorithms). Finding a funny, interesting AND socially, environmentally conscious human who also creates entertaining content is pretty rare, right? Exactly. I was hooked right away, and with 1.4 million youtube subscribers and coming up to 900k followers on instagram, I wasn’t the only one. My first point of call was watching the fantastically titled ”how to NOT destroy the planet while shopping“. There were many questions I wanted to ask, much admiration I wanted to share. So…after a quick binge of other videos, and a swift click of the subscribe button, Arden became the first in this series of interviews. Her answers didn’t disappoint. Read on, read on…
To start, could you share your name and various media handles:
@ardenrose on everything!!
In a community of hauls, where buying in excess and presenting that image to the world is commonplace, you choose to do differently. We think that’s totally awesome and also pretty brave. Was it hard for you to step away from the established way of working and suggest a different way of doing things?
It was hard in the sense that hauls tend to do well on YouTube and they’re easy (i.e. unoriginal) content to make. Honestly, buying that much junk was tiring, it filled up my closet with trendy pieces I don’t want in a month, and it was boring to make. I’m so much happier to share clothing that I had to hunt or search for to make it sustainable and worth showing on my channel! Honestly, everyone should give themselves the challenge of not relying on constantly selling their audience on cheap slave labor. Definitely helps me sleep (slightly) better at night.
Your video ‘how to NOT destroy the planet while shopping’ is SO well informed and honest and great. You mention other youtubers who inspired your choices. Do you think more people on the platform need to be addressing these issues?
ABSOLUTELY. It shocks me that people can just turn a blind eye to the obvious pain they allow corporations to get away with or ignorantly support. Everyone should be promoting sustainable business practices, especially the women on the internet that tend to to push fast fashion as a “cheap” and “easy” alternative to a constantly refreshing industry like the fashion industry. Viewers should be educated, but at the very least the entertainers who are preaching to them should be educated.
Have you always been a conscious consumer or was there a moment when the switch flipped and you started to think more about the way you buy?
I touch on this briefly in my “how to NOT destroy the planet while shopping” video, but I used to make H&M and Forever21 hauls allllll the time. Constantly. My channel was filled with that shit. Fortunately I sat down and watched all the necessary documentaries and read all of the articles late last year and completely got my stupid self educated on the issue. Honestly, I always KNEW that fast fashion was bad business, but I was wilfully ignorant so that I didn’t have to give up my shopping addiction that felt baked into my personality.

Do you see an uptake in responsibility from your followers when you share content that focuses on sustainable issues? Do their responses show that they’re thinking differently about what they buy and how they buy?
Yes!! And that’s what’s so amazing to me! I don’t even have the largest audience but I get hundreds of comments about my sustainability video a week. I didn’t even think that many people saw it! Nowadays, consumers want to be in the know, and they want clear consciences. Having a friend on the internet (me!) sitting you down and calling you out on the way you’ve been spending your money is helpful and doesn’t feel accusatory! It feels like friendly advice which is important. A lot of people get turned off of the sustainability conversation because it sounds preachy. You need to be a friend to these people, not a holier than thou asshole. I like to think I’ve helped a lot of young women and men rethink their spending habits when it comes to fashion, but I also think it’s just the power of a younger generation that actually cares about others and the planet! They’re awesome and so fired up for change!
Do you think it is easy to find and share information about the sustainability of fashion brands and the effects of fast fashion on people and planet? Is there anything you can think of that would help make it easier to do so?
It is easy if you want to find it. It would be easier if large publications and fashion houses made it a priority to promote the message. It doesn’t benefit the industry to reveal its ugly underbelly, so they try to hide it, or dangle a carrot in your face via a “sustainable line” that only happens once in a blue moon. If there was a grassroots coalition of the top fashion bloggers and instagram baddies calling these companies out and only promoting sustainable brands, I can bet you big money things would shift in a major way.
Okay now for some quick ones…
- Current favourite piece in your closet?
A brown corduroy button down dress from Paloma Wool that I bought recently. - Do you remember the first piece of clothing that you ever bought for yourself?
I would have NO idea and I find that sad. It was probably a tee-shirt from Target if I’m being honest. - Do you still have it?
Definitely not. - Do you know who made the clothes you are currently wearing?
Yes! A small company in Denmark knitted my sweater, my tee shirt is of my own design and is produced sustainably in Canada, and my leggings are from an activewear company that produces everything in a mom and pop shop out of Italy. Wearing a very well traveled outfit right now hahaha. - Top tip for others wishing to shop more responsibly?
Unless a brand *explicitly* advertises that it’s sustainable, be skeptical, and even if they do, remain skeptical. Educate yourself. We have the internet now and have 0 excuses to be ignorant! If you question the sustainability of a brand, do a quick google search before committing to the purchase. It’s true that sustainable fashion tends to be a bit pricier but just think about all the hands that it took to create the piece you’re holding and the people they belong to that are being paid well and treated with respect because you’re willing to treat your closet with respect. We don’t NEED an abundance of new clothes every season, we’ve been duped by an industry that only has money in mind. You don’t have to have the latest trend in your closet, you can re-wear clothes until they fall off your body, and anyone who judges you for your lifestyle is slow on the uptake.
Thanks, Arden 🙂
Check back every month for more in the Power of Influence series. We’ll post a new entry on the last day of each month throughout 2019. If you think there is someone we should be talking to, drop us a line on instagram.
We host Fashion Revolution Week in April of every year. This year kicks off on the 22nd of April. Throughout the week we encourage people to ask brands ‘who made my clothes’ in hopes of shining a light on the unknowns of the fashion industry. By doing this, we hope to shift the focus from consumers to brands, and to all the hands involved, be it producers, workers, farmers or otherwise. We track the reach and impact of collaborators throughout Fashion Revolution Week and use the findings to fight for change worldwide, through government and policy. We would hugely appreciate it if you would be willing to share a story or celebrate a brand you love or simply ask #whomademyclothes during Fashion Revolution Week in 2019.







